1. Hydrogen sulfide is composed of two elements: hydrogen and sulfur. In an experiment,
4.965 g of hydrogen sulfide is fully decomposed into its elements.
- a) If 0.278 g of hydrogen are obtained in this experiment, how many grams of sulfur must be obtained?
- In accordance to the law of conservation of mass, 0.278 g H2 + (x) g S = 4.965 g H2S. Solve for x. The answer is 4.687 g S (to 2 significant figures).
- b) What fundamental law does this experiment demonstrate? (Answer: The Law of Conservation of Mass)
- c) How is this law explained by Dalton's atomic theory? (Answer: Atoms are neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction).
2. In a series of experiments, a chemist prepared three different compounds that contain only iodine and fluorine and determined the mass of each element in each compound.
| compound | mass of iodine (g) | mass of fluorine (g) |
| 1 | 4.75 | 3.56 |
| 2 | 7.64 | 3.43 |
| 3 | 9.41 | 9.86 |
- a) Calculate the mass of fluorine per gram of iodine in each compound.
- compound 1
- (3.56 g F) / (4.75 g I) = 0.749 / g (to 3 significant figures)
- compound 2
- (3.43 g F) / (7.64 g I) = 0.449 / g (to 3 significant figures)
- compound 3
- (9.86 g F) / (9.41 g I) = 1.05 / g (to 3 significant figures)
- How do the numbers in part (a) support the atomic theory? (Answer: 5:3:7, they satisfy the law of multiple proportions).
3. A negatively charged particle is caused to move between two electrically charged plates, as illustrated below.
- a) Why does the path of the charged particle bend? (Answer: its charge and the charges on the plates)
- b) As the charge on the plates is increased, would you expect the bending to increase, decrease, or stay the same? (Answer: increase)
- c) As the mass of the particle is increased while the speed of the particles remains the same, would you expect the bending to increase, decrease, or stay the same? (Answer: decrease)
- d) An unknown particle is sent through the apparatus. Its path is deflected in the opposite direction from the negatively charged particle, and it is deflected by a smaller magnitude. What can you conclude about this unknown particle? (Select all that apply.) (Answers: The particle has greater mass than the electron AND The particle is positively charged)
4. The radius of the
rubidium (Rb) atom is about
2.1 
.
- a) Express this distance in nanometers (nm).
- (2.1 A / 1) * (1.0e-10 m / 1 A) * (1.0e9 nm / 1 m) = 0.21 nm (to 2 significant figures)
- b) Express this distance in picometers (pm).
- (2.1 A / 1) * (1.0e-10 m / 1 A) * (1,000,000,000,000 pm / 1 m) = 210 pm (to 2 significant figures)
- c) How many rubidium (Rb) atoms would have to be lined up to span 1.0 mm?
- The radius of the rubidium atom is 2.1 A, so its diameter is 4.2 A.
- (1.0 mm / 1) * (1 m / 1000 mm) * (1 A / 1.0e-10 m) * (1 atom / 4.2 A) = 2.4e6 Rb atoms (to 2 significant figures)
- d) If the atom is assumed to be a sphere, what is the volume in cm3 of a single rubidium (Rb) atom?
- The volume of a sphere is (4/3)π*r3. Calculate the volume in angstroms:
- v = (4/3)π*(2.1 A)3 = 38.7924 A3
- Now convert the volume in angstroms to cubic centimeters:
- (38.7924 A3 / 1) * (1.0e-10 m / 1 A)3 * (100 cm / 1 m)3 = 3.9e-23 cm3 (to 2 significant figures)
5.
- a) Give the mass number of a tungsten atom with 110 neutrons.
- Mass number = protons + neutrons = 74 protons + 110 neutrons = 184
- b) Give the mass number of an iron atom with 30 neutrons.
- Mass number = protons + neutrons = 26 protons + 30 neutrons = 56
- c) Give the mass number of an americium atom with 148 neutrons.
- Mass number = protons + neutrons = 95 protons + 148 neutrons = 243
6. Radioactive americium-241 is used in household smoke detectors and in bone mineral analysis. Give the number of electrons, protons, and neutrons in an atom of americium-241.
- a) electrons
- The number of electrons of a neutrally charged atom is the same as its number of protons. The answer is 95.
- b) protons
- The number of protons is equal to the atomic number found on the periodic table. The answer is 95.
- c) neutrons
- The mass number = protons + neutrons. 241 = 95 protons + x neutrons. The answer is 146.
7. Strontium has four stable isotopes. Strontium-84 has a very low natural abundance, but
86Sr,
87Sr, and
88Sr are all reasonably abundant. Knowing that the atomic weight of strontium is 87.62, which of the more abundant isotopes predominates?
- (The atomic weight will be closest to the isotope with the greatest abundance. The answer is 88Sr, since 87.62 is closest to 88).
8. Magnesium has three naturally occurring isotopes.
24Mg (23.985 amu) with 78.99% abundance,
25Mg (24.986 amu) with 10.00% abundance, and a third with 11.01% abundance. Look up the atomic mass of magnesium, and then calculate the mass of the third isotope.
- The atomic weight is a weighted average of each of an element's isotopes.
- (23.985 amu * 0.7899) + (24.986 amu * 0.1) + (x amu * 0.1101) = Atomic weight
- (23.985 amu * 0.7899) + (24.986 amu * 0.1) + (x amu * 0.1101) = 24.3050
- Solve for x. The answer is 26 amu (to 2 significant figures)
9.
a) What particle did James Chadwick's experiments discover? (Answer: Neutron)- b) In what part of the atom is this particle located? (Answer: Nucleus)
10.
- a) Which scientist's experiment indicated that the atom is mostly empty space and rejected the 'plum pudding' atomic model? Enter only the last name. (Answer: Rutherford)
- b) What metal did he use in the experiment? (Answer: Gold)
11. Complete the table.
| Isotope | % Natural Abundance | Atomic Mass (amu) | Average Atomic Mass (amu) |
| copper-63 | 69.17 | 62.929599 |
|
| copper-65 | 30.83 | 64.927793 |
- Atomic mass is a weighted average of the abundance of the isotopes of an element multiplied by the atomic masses of the isotopes.
- (69.17 amu * 0.62929599) + (30.83 * 0.64927793) = 63.55 amu (to 4 significant figures)
12. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are there in
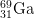 3+
3+?
- a) protons
- The number of protons is equal to the atomic number found on the periodic table. The answer is 31.
- b) neutrons
- The mass number = protons + neutrons. 69 = 31 protons + x neutrons. The answer is 38.
- c) electrons
- The number of electrons of an ion with a +3 charge is equal to the number of electrons in a neutral atom minus 3, as the plus indicates negative charge has been lost. 31 electrons - 3 = 28 electrons.
13. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are there in
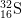 2-
2-?
- a) protons
- The number of protons is equal to the atomic number found on the periodic table. The answer is 16.
- b) neutrons
- The mass number = protons + neutrons. 32 = 16 protons + x neutrons. The answer is 16.
- c) electrons
- The number of electrons of an ion with a -2 charge is equal to the number of electrons in a neutral atom plus 2, as the minus indicates negative charge has been gained. 16 electrons + 2 = 18 electrons.
14. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are there in
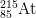 1-
1-?
- a) protons
- The number of protons is equal to the atomic number found on the periodic table. The answer is 85.
- b) neutrons
- The mass number = protons + neutrons. 215 = 85 protons + x neutrons. The answer is 130.
- c) electrons
- The number of electrons of an ion with a -1 charge is equal to the number of electrons in a neutral atom plus 1, as the minus indicates negative charge has been gained. 85 electrons + 1 = 86 electrons.
 .
. 2.7
2.7  11 hands?
11 hands? 10-2
10-2 10-6
10-6 10-4
10-4 10-9
10-9 10-7
10-7 10-10
10-10 109
109 1.0 ft, what is the average thickness of the sheet in meters?
1.0 ft, what is the average thickness of the sheet in meters?  10-3 km (Answer: 4)
10-3 km (Answer: 4) 105) - (3.400
105) - (3.400  103)]
103)]  2.8944 (Answer: 8.260e7) (to 4 significant figures)
2.8944 (Answer: 8.260e7) (to 4 significant figures) 20014.0) + (3200.
20014.0) + (3200.  40.) (Answer: 1.3e5) (to 2 significant figures)
40.) (Answer: 1.3e5) (to 2 significant figures) [1242 - (3.52
[1242 - (3.52  100.)] (Answer: 7.63e5) (to 3 significant figures)
100.)] (Answer: 7.63e5) (to 3 significant figures)